You can use the BigQuery web UI as a visual interface to complete tasks like running queries, loading data, and exporting data. This quickstart shows you how to query public tables and load sample data into BigQuery.
Prerequisites
To use the BigQuery web UI, your account needs to have access to a BigQuery-enabled project in the Google Developers Console. If you haven't used the Developers Console before, go to the console, accept the terms of service, and create a new project. Then, you'll be able to access the BigQuery web UI.
To complete the second half of this quickstart, loading data into a table, you'll need to also set up billing. The cost of running the loading data exercise is negligible (less than $0.01, based on storage costs). You can query a public dataset without setting up billing as long as you stay in the free tier for queries.
To set up billing, go to the console and click Billing in the navigation.
Query a public dataset
The BigQuery web UI provides an interface to query tables, including public tables offered by BigQuery.
Click the COMPOSE QUERY button.
-
Copy and paste the following query into the New Query text area:
SELECT weight_pounds, state, year, gestation_weeks FROM publicdata:samples.natality ORDER BY weight_pounds DESC LIMIT 10;
-
Click the circular icon to activate the query validator.
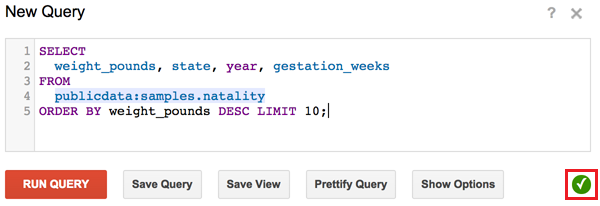
A green or red section displays above the buttons depending on if the query is valid or invalid. If valid, the validator also describes the amount of data that will be processed once you run the query. This is helpful for determining how much a query will cost to run.
-
Click the RUN QUERY button. The query results display underneath the buttons.

The above query accesses a table from a public dataset that BigQuery provides.
In the identifier publicdata:samples.natality:
publicdatais the project namesamplesis the dataset namenatalityis the table name
You can browse the schema of other public tables by clicking publicdata:samples in the navigation. The expanded list of titles are all of the public tables you can query against.
Load data into a table
Next, we'll load custom data into a table and run a query against it.
Download custom data
Download this zip file (approximately 7 MB). The file contains data about popular baby names and is provided by the US Social Security Administration. Unzip the file onto your hard drive.
The zip file contains a read me file that describes the dataset schema. Learn more about the dataset.
Create a dataset
Next, create a dataset in the web UI to hold the data.
Click the down arrow icon
 next to your project name in the navigation, then click Create new dataset.
next to your project name in the navigation, then click Create new dataset.-
Input a dataset ID.
Dataset IDs are unique on a per-project basis, so ensure that the ID you choose isn't already listed under your project name in the navigation. Click the question mark icon to see ID limitations.
Load the data into a new table
Next, load the data into a new table.
-
In the navigation, hover on the dataset ID that you just created. Click the down arrow icon
 next to the ID and click Create new table.
next to the ID and click Create new table. -
Input a table ID. Click the question mark icon to see ID limitations. After inputting the ID, click the Next button.
-
Click the Choose file button. Navigate to the data you unzipped in the step above, and select one of the
yob****.txtfiles. Then, click the Next button. -
Copy and paste the following string into the Schema input:
name:string,gender:string,count:integer -
Click the Submit button.
Once you complete the above steps, BigQuery creates a table and loads the data into it. While BigQuery loads the data, a (loading) string displays after your table name in the navigation. The string disappears once the data has been fully loaded.
Query the table
Now that we've loaded custom data into a table, you can run queries against it. The process is identical to the query a public dataset example above, except that this time, we're querying your custom table instead of a public table.
Click the COMPOSE QUERY button.
-
Copy and paste the following query into the New Query text area. Replace projectId, datasetId, and tableId with the custom IDs you chose above.
SELECT name, count FROM projectId:datasetId.tableId WHERE gender = 'M' ORDER BY count DESC LIMIT 5;
The above query displays the top 5 men's names for the year of data you loaded into the table.
