Google Cloud SQL supports connecting to an instance using the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol. After you create an instance, we recommend that you configure it so that you can connect to it using SSL. After following the configuration steps below, you will have all the necessary certificate and key files you need to establish a secure connection. For more information about using SSL connection with MySQL, see Using SSL Connections in the MySQL Reference Manual.
Connections between Cloud SQL and App Engine are always encrypted; you do not need to create client certificates for them.
To create a client SSL certificate:
Developers Console
- Go to the Google Developers Console and select a project by clicking on the project name.
- In the sidebar on the left, click Storage > Cloud SQL to show a list of Cloud SQL instances for the project.
- Select an instance to configure by clicking the instance name.
- Click Access Control > SSL.
- [Optional] In the SSL Connections section, click Allow only SSL connection to enforce that only SSL connections can connect to the instances.
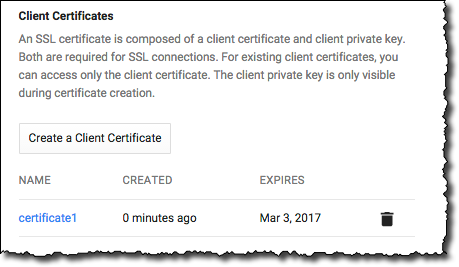
- In the Client Certificates section, click
Create a Client Certificate.
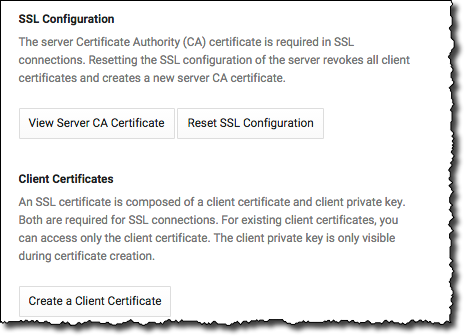
Figure 1: Instance SSL options. - In the New client certificate dialog box, give the certificate a unique name and click Add.
- In the first panel of the New SSL Certificate created dialog box, copy the certificate private key to a file, for example, client-key.pem, and store it securely. Be sure to copy all of the key, including the first line "-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----" and last line "-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----".
- In the second panel of the New SSL Certificate created
dialog box, copy the client
certificate to a file, for example, client-cert.pem, and
save it.
Be sure to copy all of the certificate, including the first line "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----" and the last line "-----END CERTIFICATE-----". Unlike the private key, you can return to the Google Developers Console and view the certificate.
- In the third panel of the New SSL Certificate created dialog box, copy server CA certificate, for example, server-ca.pem, and save it.
- Click Close and Restart to close the instance and
restart the instance immediately or click Close and
manually restart the instance later.
A restart of the instance is required to enable the certificate.
- If you did not choose Close and Restart, then restart the instance to enable the certificate.
At this point, you have enabled the instance to use SSL and you have:
- A CA certificate saved as server-ca.pem.
- A client public key certificate saved as client-cert.pem.
- A client private key saved as client-key.pem.
Depending on which tool you use to connect, these three items are specified
in different ways. For example, when connecting using MySQL client, these three
files are the values for the --ssl-ca, --ssl-cert, and
--ssl-key command options, respectively. For an example connection
using MySQL client and SSL, see
Connecting with MySQL Client.
Cloud SDK
- Install the Cloud SQL command line if you haven't already (see Managing Instances Using the Cloud SDK).
- Set the project to the one that contains the instance to for which you
want to configure SSL.
$ gcloud config set project YOUR_PROJECT_ID
- [Optional] Configure the instance so that mysqld should default to
REQUIRE X509for users connecting over IP.$ gcloud sql instances patch YOUR_INSTANCE_NAME --require-ssl $ gcloud sql instances restart YOUR_INSTANCE_NAME
The second command restarts the instance to apply the configuration change.
- Creates an SSL certificate using the
ssl-certs createcommand.$ gcloud sql ssl-certs --instance YOUR_INSTANCE_NAME create CERT_NAME client-key.pem
- Retrieve the server public key certificate you just created with the
ssl-certs describecommand.$ gcloud sql ssl-certs --instance YOUR_INSTANCE_NAME describe --format text CERT_NAME
Be sure to copy all of the certificate, from the first line "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----" to the last line "-----END CERTIFICATE-----" to a file, for example
client-cert.pem. - Get the server certificate using the
instances describecommand.$ gcloud sql instances describe YOUR_INSTANCE_NAME --format text
Be sure to copy all of the certificate, from the first line "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----" to the last line "-----END CERTIFICATE-----" to a file, for example
server-ca.pem. - Restart the instance to enable the certificate.
$ gcloud sql instances restart YOUR_INSTANCE_NAME
Now you have:
- A server private key,
client-key.pem. - A server public key certificate,
client-cert.pem. - A server certificate,
server-ca.pem.
With these three items, you can connect to your instance using SSL. For examples, see Connecting Using MySQL Client and Admin and Reporting Tools.
To get details about a client SSL certificate:
For an existing client certificate, you can view the client certificate (client-cert.pem) and the server CA certificate (server-ca.pem).You cannot recover the client SSL private key (client-key.pem) after the certificate is created. If you lost the private key, you must create a new key.
Developers Console
- Go to the Google Developers Console and select a project by clicking on the project name.
- In the sidebar on the left, click Storage > Cloud SQL to show a list of Cloud SQL instances for the project.
- Select the instance that contains the client SSL certificate you want to get information about.
- Click Access Control > SSL.
- In the Client Certificates section, select a certificate to see the client certificate (client-cert.pem).
- In the SSL Configuration section, click View Server CA Certificate to view the CA certificate (server-ca.pem).
Cloud SDK
- Install the Cloud SQL command line if you haven't already (see Managing Instances Using the Cloud SDK).
- Set the project to the one that contains the instance to for which you
want to configure SSL.
$ gcloud config set project YOUR_PROJECT_ID
- Retrieve the server public key certificate you just created with the
ssl-certs describecommand.$ gcloud sql ssl-certs --instance YOUR_INSTANCE_NAME describe --format text CERT_NAME
Be sure to copy all of the certificate, from the first line "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----" to the last line "-----END CERTIFICATE-----" to a file, for example
client-cert.pem. - Get the server certificate using the
instances describecommand.$ gcloud sql instances describe YOUR_INSTANCE_NAME --format text
Be sure to copy all of the certificate, from the first line "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----" to the last line "-----END CERTIFICATE-----" to a file, for example
server-ca.pem.
To delete a client SSL certificate:
Developers Console
- Go to the Google Developers Console and select a project by clicking on the project name.
- In the sidebar on the left, click Storage > Cloud SQL to show a list of Cloud SQL instances for the project.
- Select the instance that contains the client SSL certificate you want to delete.
- Click Access Control > SSL.
- In the Client Certificates section, find the certificate
you want to delete and click delete
 .
. - In the Delete client certificate dialog box, click OK.
Cloud SDK
- If needed, set the project to the one that contains the instance for
which you want to configure SSL.
$ gcloud config set project YOUR_PROJECT_ID
- Delete the SSL certificate using the
ssl-certs delete
command.
$ gcloud sql ssl-certs delete CERT_NAME
